sociogenomics2023
Lab 2. Getting started with Plink
Installing Plink in your system
PLINK is a free, open-source software package for genomic data analysis. It was originally designed for analyzing genetic association studies, particularly for case-control studies and family-based studies. PLINK can perform various tasks related to genetic data analysis, including data management, quality control, association analysis, haplotype analysis, and population stratification correction.
PLINK is widely used in the field of human genetics and has been cited in numerous scientific publications. It is compatible with various file formats commonly used in genetics research, such as VCF, BED, and PED formats. PLINK is available for download on the project’s website and is actively maintained by a team of developers.
Let’s start from our home directory and change directory to Sociogenomics/Software
cd $HOME
cd Sociogenomics/Software
PLINK is available from here: We use (for now) PLINK 1.9. Now we can download the linux version in our system
wget https://s3.amazonaws.com/plink1-assets/plink_linux_x86_64_20230116.zip
unzip plink_linux_x86_64_20230116.zip
let’s check file permission. We need to make plink executable to use it as software
ls -l
Check file permissions
- chmod +rwx filename to add permissions.
- chmod -rwx directoryname to remove permissions.
- chmod +x filename to allow executable permissions.
- chmod -wx filename to take out write and executable permissions.
This is how we make the file executable
chmod +x plink
we can now execute the software using ./ in front of the file
./plink --help
Create symbolic links
A symbolic link, also known as a symlink or a soft link, is a type of file that acts as a pointer or reference to another file or directory in a file system.
When a symbolic link is created, it contains the path to the file or directory that it points to. When a user accesses the symbolic link, the file system follows the link and accesses the file or directory that it points to, as if the user had accessed it directly.
Symbolic links are often used in Unix-based operating systems, such as Linux or macOS, to create shortcuts to frequently used files or directories, or to provide a simpler or more intuitive file structure. They can also be used to create multiple paths to the same file or directory, or to enable compatibility between different versions of software.
cd $HOME/Sociogenomics
ln -s Software/plink
Now we can access PLINK from this directory
pwd
./plink --help
Upload the file week2.zip and unzip files in Data folder
cd Data/
unzip week2.zip
mv week2/*.* ./
rm -r __MACOSX/
rm -r week2
cd $HOME/Sociogenomics
How to read PLINK files
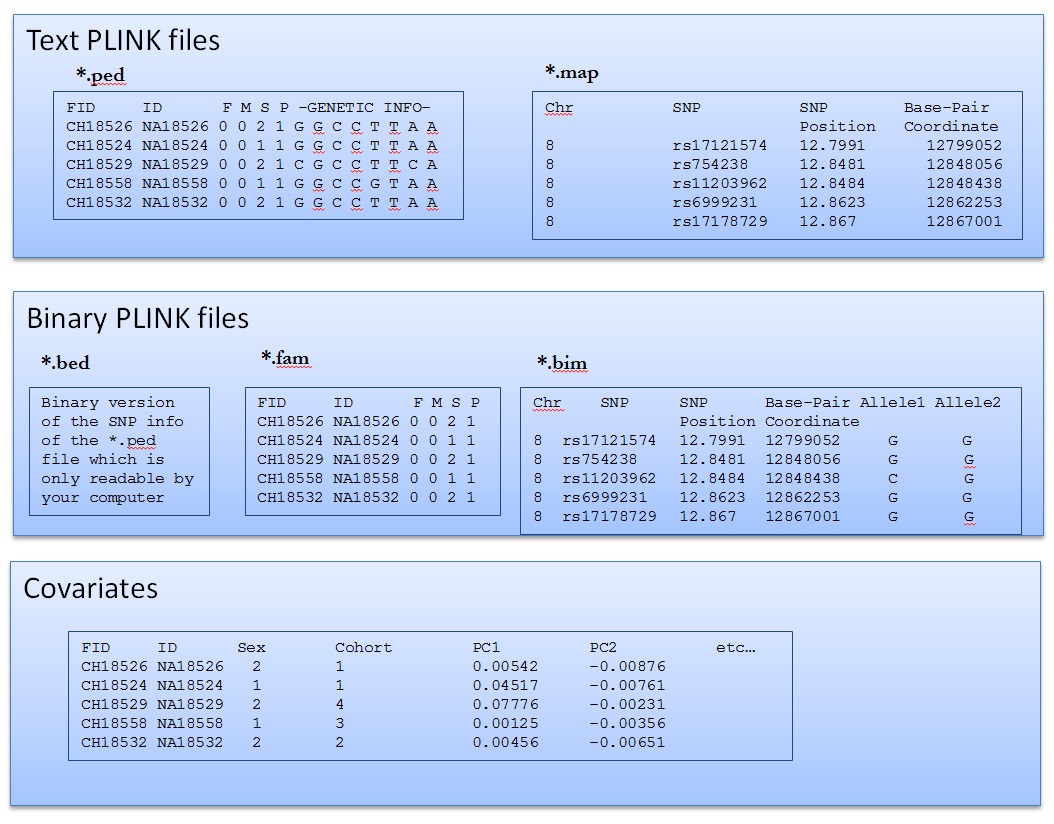
Read Binary PLINK file
we start with PLINK binary files
.bimfile contains info on the markershead Data/hapmap-ceu.bim.famfile contains info on the individualshead Data/hapmap-ceu.fam.bedfiles are not readable!head Data/hapmap-ceu.bedRecode PLINK file
Recode into map and ped files
./plink --bfile Data/hapmap-ceu --recode --out Results/hapmap-ceu
.mapfile contains info on the markers
head Results/hapmap-ceu.map
.pedfile contains info on the individual genotypeshead -1 Results/hapmap-ceu.ped
###Import VCF into plink A VCF (Variant Call Format) file is a standard file format used in bioinformatics to store genetic variation data, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and insertions/deletions (indels), typically obtained from DNA sequencing. It contains information about the genomic location, alleles, genotype, and quality score of each variant called.
./plink --vcf Data/ALL.chr21.vcf.gz --make-bed --out Results/test_vcf
Select individuals
./plink --bfile Data/hapmap-ceu \
--keep Data/list.txt \
--make-bed --out Results/selectedIndividuals
Select individuals with genotype at least 95% complete
We can select individuals based on the completness of their genotype
./plink --bfile Data/hapmap-ceu --make-bed --mind 0.05 --out Results/highgeno
Select specific markers
In this way we select only a specific marker, in this case SNP rs9930506
./plink --bfile Data/hapmap-ceu \
--snps rs9930506 \
--make-bed \
--out Results/rs9930506sample
Merge genetic files
We can merge different files (different set of individuals, in this case)
./plink --bfile Data/HapMap_founders \
--bmerge HapMap_nonfounders \
--make-bed --out Results/merged_file
Add a phenotype into PLINK files
PLINK file can also store info on a phenotype
head Data/1kg_EU_qc.fam
head Data/1kg_EU_qc.bim
This file contains info on BMI of different individuals
head Data/BMI_pheno.txt
This is how we add a phenotipic information to a plink file
./plink --bfile Data/1kg_EU_qc \
--pheno Data/BMI_pheno.txt \
--make-bed --out Results/1kg_EU_BMI
head Data/1kg_EU_BMI.fam
Descriptive Statistics
Allele frequency
We can calculate allele frequency
./plink --bfile Data/hapmap-ceu --freq --out Results/Allele_Frequency
head Results/Allele_Frequency.frq
Missing values
individuals
./plink --bfile Data/hapmap-ceu --missing --out Results/missing_data
variants
head Data/missing_data.imiss
Filter females
./plink --bfile Data/hapmap-ceu \
--filter-females \
--make-bed \
--out Results/hapmap_filter_females
